
- #Periodic table chemistry subject test series#
- #Periodic table chemistry subject test free#
#Periodic table chemistry subject test free#
Topics may include: introduction to entropy, Gibbs free energy and thermodynamic favorability, thermodynamic and kinetic control free energy and equilibrium, galvanic (voltaic) and electrolyte cells, electrolysis and Faraday’s law.Ĭheck out our AP Chemistry Prep and ASAP Chemistry books for a comprehensive content review AP Chem Question Types Multiple-Choice
Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics. Topics may include: introduction to acids and bases, pH and pOH of strong acids and bases, acid-base reactions and buffers, molecular structure of acids and bases, pH and pK a, properties of buffers. Topics may include: introduction to equilibrium, calculating the equilibrium constant, calculating equilibrium concentrations, introduction to Le Chatelier’s principle, introduction to solubility equilibria, pH and solubility, free energy of dissolution. Topics may include: endothermic and exothermic processes, heat transfer and thermal equilibrium, heat capacity and calorimetry, energy of phase changes, introduction to enthalpy of reaction, enthalpy of formation, Hess’s law. Topics may include: reaction rate, introduction to rate law, elementary reactions, collision model, introduction to reaction mechanisms, multistep reaction energy profile, and catalysis. 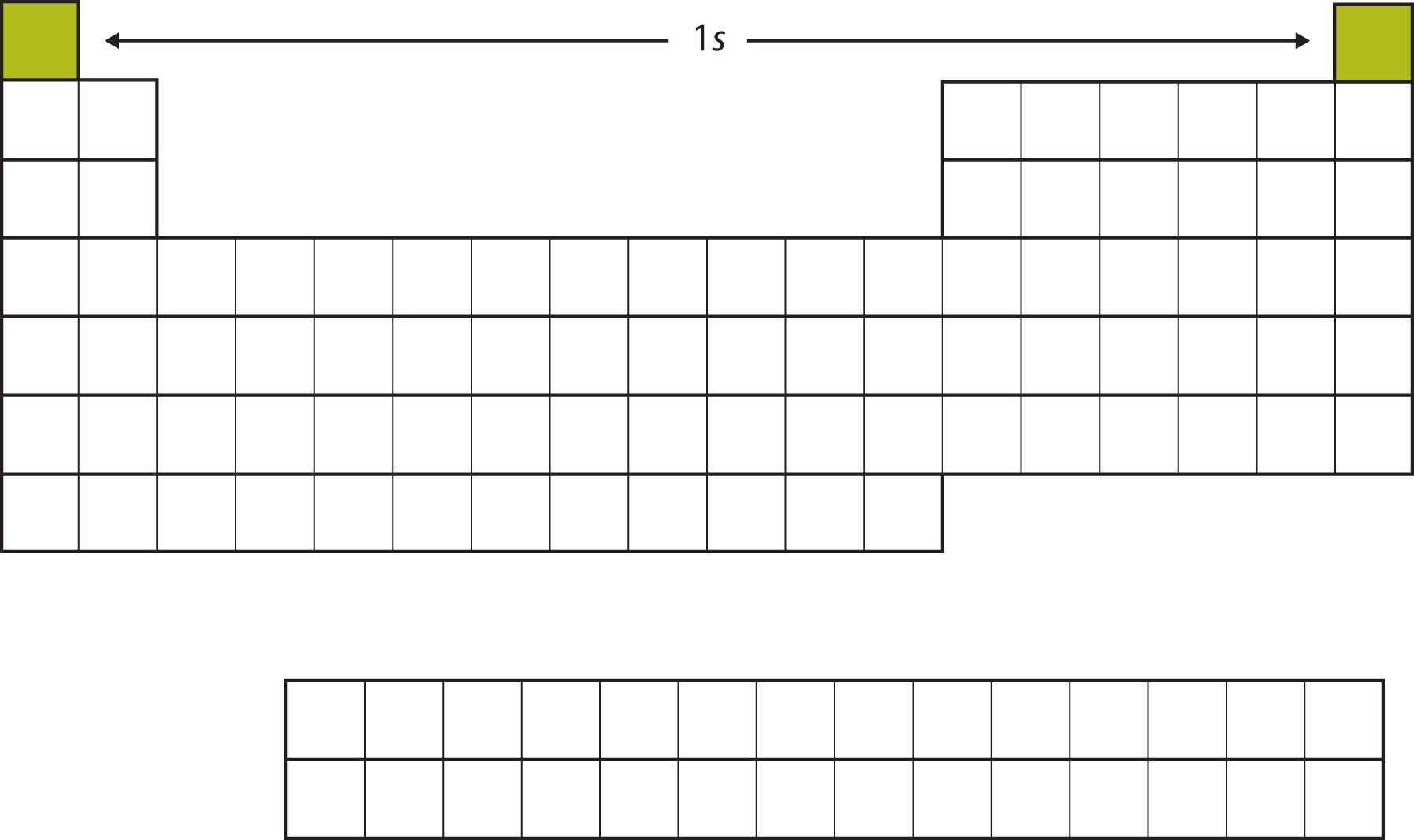
Topics may include: introduction for reactions, net ionic equations, representations of reactions, physical and chemical changes, stoichiometry, types of chemical reactions. Topics may include: intermolecular forces, solids, liquids, and gases, kinetic molecular theory, solutions and mixtures, photoelectric effect.
Unit 3: Intermolecular Forces and Properties. Topics may include: types of chemical bonds, intramolecular force and potential energy, structure of ionic solids, structure of metals and alloys, Lewis diagrams, resonance and formal charge, VSEPR and bond hybridization. Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties. Topics may include: moles and molar mass, mass spectroscopy of elements, elemental composition of pure substances, composition of mixtures, atomic structure and electron configuration, photoelectron spectroscopy, periodic trends, valence electrons and ionic compounds. Unit 1: Atomic Structure and Properties. The topics of the AP Chemistry Exam are grouped into nine Units. Read More: Review for the exam with our AP Chemistry Cram Course AP Chem Review: Topics Private Tutoring with Pass Assurance NEW. Over time a color scheme has been added to the periodic chart to help understand which elements belong to named categories. The noble gases have low melting and boiling points. While groups and periods are useful in understanding the chemical families, elements are also seen as being organized by blocks.  Groups are the horizontal rows and represent families of elements.
Groups are the horizontal rows and represent families of elements. #Periodic table chemistry subject test series#
Each compound is represented by a square on the Periodic Table and each is denoted by its own unique series of letters. …………… are noted by the vertical column and represent families of elements. The…………… ……….… is the average mass of the protons, electrons and neutrons in a single atom. represents the number of protons in the nucleus or the electrons orbiting the nucleus. (number of protons), electron configurations, and their chemical The periodic tableis an organized arrangement of the chemical elements, in order of their …………………. So in order to finish it quickly he constructed a table of all the elements according to their atomic weights to understand the elements better and to complete his work easily. Dmitry Mendeleev was supposedly late in submitting his work on 63 elements. Mercury and bromine are only two elements that are liquid in room temperature. Periodic table of Mendeleev is in the ascending as order of atomic weight and the modern periodic table is according to increasing atomic number. 75% of the elements on the periodic table are metals. Its basic uses are to locate bone cancers in x-rays. The first man-made element is Technetium. The Noble Gases Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are unreactive. The atomic weight of Uranium is 238 being the heaviest element. The lightest element is Hydrogen its atomic weight is 1 and that is why it is found in the top left corner of the periodic table. The only metal which is so soft that it can be to cut with a knife and light enough to float on water is Lithium. 
The International Union of Pure Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) is takes care of the periodic table. 90 elements are found in nature, and others are man-made. There are a total of 118 elements in the periodic table. It is called the periodic table because the rows are called periods.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
